How to uninstall wsl?
Contents
- 1 What is wsl?
- 2 PROS and CONS of WSL
- 3 When to Use WSL
- 4 When to Avoid WSL
- 5 How to uninstall wsl?
- 6 Conclusion
What is wsl?
WSL stands for Windows Subsystem for Linux, a feature in Windows 10 and Windows 11 that enables you to run a full Linux distribution directly on your Windows machine without the need for a virtual machine or dual boot setup.
Key Features of WSL:
- Linux on Windows: WSL allows you to run a complete Linux environment (including most command-line tools, utilities, and applications) natively on your Windows computer. This is especially useful for developers who need to use Linux tools, bash scripting, or run server-side applications while working on a Windows system.
- Two Versions of WSL:
- WSL 1: The first version of WSL runs a Linux-compatible kernel interface on top of the Windows kernel. It allows you to run Linux binaries, but it doesn’t provide the full Linux kernel experience. Instead, it translates Linux system calls to Windows system calls.
- WSL 2: Introduced with Windows 10 version 2004 and later, WSL 2 runs a real Linux kernel in a lightweight virtual machine (VM). This offers better performance, full system call compatibility, and support for running more complex applications, such as Docker containers.
- Integration with Windows: WSL allows seamless integration between Windows and Linux environments:
- You can access your Windows files from within Linux and vice versa.
- You can use Linux tools alongside your Windows applications, and even run Linux scripts within Windows programs.
- Use Cases:
- Development: Many developers use WSL to work on Linux-specific code or development tools, such as using Node.js, Python, or Ruby in their native environments, or working on web applications.
- Running Command-Line Tools: WSL lets you run Linux command-line utilities and software directly on Windows.
- Docker and Virtualization: WSL 2 allows developers to run Docker containers natively on Windows, making it much easier to build, run, and manage containerized applications.
- Installation and Usage:
- WSL is available on Windows 10 (version 1903 and above) and Windows 11. You can install it via the Microsoft Store, or enable it using the command line (through PowerShell or Windows Terminal).
- Once installed, you can choose your preferred Linux distribution, such as Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, or others, directly from the Microsoft Store.
Why Use WSL?
- Linux Tools on Windows: It allows you to use powerful Linux tools (like bash scripting, Git, and more) alongside Windows applications.
- No Need for Dual Boot: Unlike dual-booting, WSL lets you run both Windows and Linux applications simultaneously without needing to reboot your system.
- Better for Development: Developers can test Linux-specific applications or scripts on a Windows system without needing a separate Linux machine or VM.
- Low Overhead: WSL 2 offers near-native Linux performance without requiring a full virtual machine, making it much lighter on resources than traditional VM solutions like VirtualBox or VMware.
PROS and CONS of WSL
Pros
- You can choose from a variety of Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, Kali Linux, and more, making it easy to set up an environment that suits your needs.
- WSL is completely free to use and easy to install on Windows 10 and 11. It can be installed via the Microsoft Store or using the command line, and setting up a Linux distribution is simple.
- WSL 2 fully supports Docker, allowing you to run Docker containers natively in a Linux environment on Windows without needing a heavy VM like Docker Desktop.
- WSL 2 uses a lightweight virtual machine, which offers better performance than WSL 1, but still uses fewer resources than a full Linux VM.
- Compared to traditional virtual machines, WSL (especially WSL 2) uses far fewer resources. This makes it a more lightweight solution for running Linux on Windows.
- Unlike traditional dual boot setups, WSL allows you to run Linux and Windows applications side by side, without the need to reboot your computer.
- Useful for developers who need Linux tools for tasks like scripting, software development, and debugging.
- WSL allows you to run Linux command-line tools (such as
bash,git,awk,sed, etc.) directly on a Windows machine without needing a full Linux installation.
Cons
- WSL 1 lacks full system call compatibility and does not use a full Linux kernel, limiting its ability to run certain applications, especially those that rely on advanced system calls or specific kernel features.
- Operations on mounted Windows file systems (e.g.,
/mnt/c/) can experience higher latency compared to native Linux file systems. - WSL integrates with Windows, but some Windows-specific apps (especially legacy software) may not work well within a Linux environment. Similarly, Linux applications within WSL might not have the same capabilities as they would on a native Linux machine.
- Not all Linux software is compatible with WSL, particularly software that requires access to lower-level system resources, specific drivers, or certain kernel modules that WSL doesn’t support.
- Performance for graphics-intensive applications may not be as good as a native Linux or dedicated virtual machine setup.
- WSL does not have full access to certain hardware resources. For example, GPU support was initially limited (though it has been improved recently), and certain peripherals may not be fully compatible.
- Certain kernel features and advanced system configurations may not work as expected.
- While WSL 2 offers a real Linux kernel, it’s still running within a Windows environment and may not support every Linux feature or configuration you would find on a native Linux installation.
When to Use WSL
- Development: Ideal for developers working on cross-platform applications or using Linux-based tools on Windows.
- Learning Linux: WSL provides a simple and safe environment to explore Linux without needing to install a separate OS.
- Docker/Containerization: Excellent for running Docker containers natively on Windows without using heavy virtual machines.
When to Avoid WSL
- High-Performance Computing: If you need hardware acceleration (e.g., GPU support) or need to work with specialized hardware, WSL might not be sufficient.
- Complex Kernel Modules: For users who need access to specific Linux kernel features or modules not available in WSL, a native Linux machine or a full VM might be a better option.
How to uninstall wsl?
1. Uninstall WSL from Windows Settings (Windows 10 and 11)
For Windows 10:
- Open Settings:
- Press
Win + Ito open Settings. - Go to Apps > Optional Features.
- Press
- Find WSL:
- Scroll through the list to find Windows Subsystem for Linux (or any installed Linux distributions, e.g., Ubuntu).
- Uninstall:
- Click on Windows Subsystem for Linux or the distribution you want to remove.
- Click Uninstall.
- Restart Your PC:
- After uninstalling, restart your computer to ensure all processes are stopped.
For Windows 11:
- Open Settings:
- Press
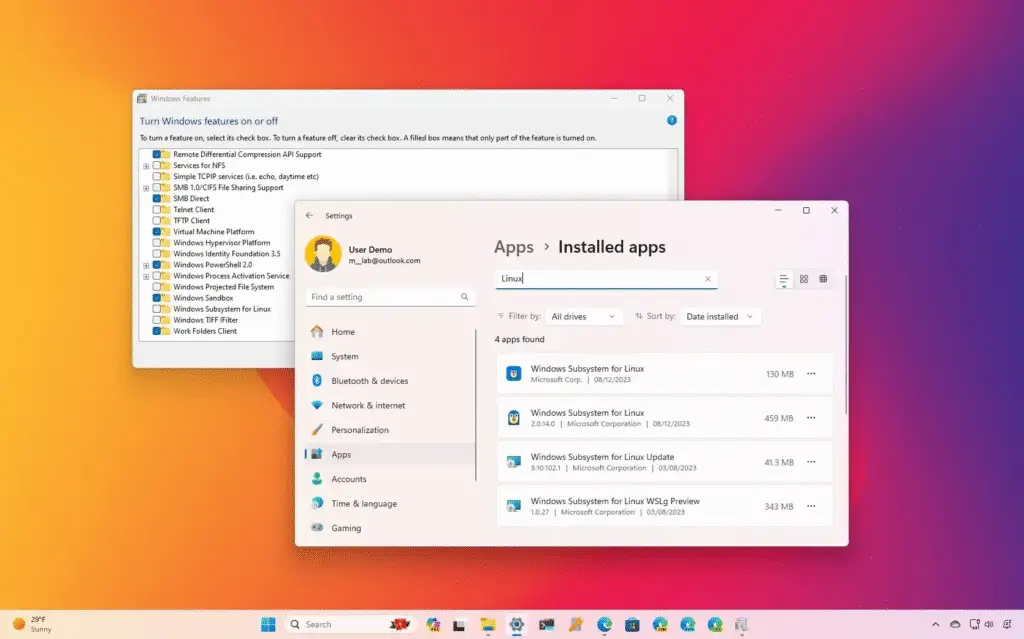
Win + Ito open Settings. - Navigate to Apps > Installed Apps.
- Press
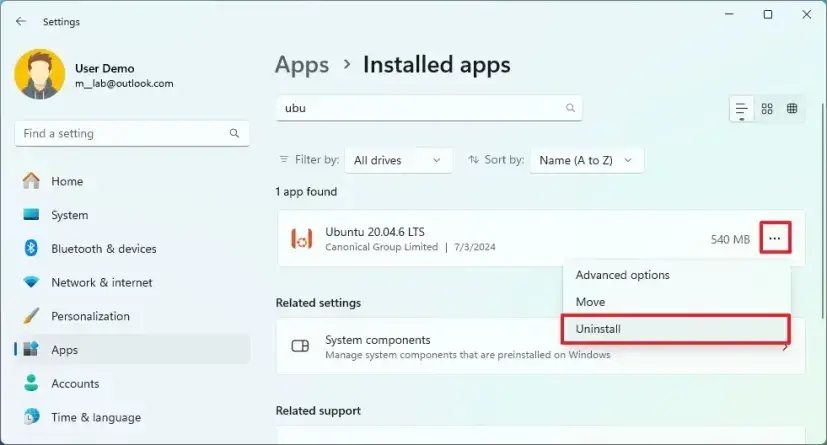
- Find the Linux Distribution:
- Look for any installed Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, etc.
- Uninstall:
- Click the three dots next to your desired distribution and select Uninstall.
- Restart Your PC:
- Restart your computer.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Uninstall WSL via PowerShell (For More Advanced Users)
If you want to fully remove WSL, including its components, follow these steps.
- Open PowerShell:
- Press
Win + X, and choose Windows Terminal (Admin) or PowerShell (Admin).
- Press
- Unregister WSL Distributions:
To uninstall a specific WSL distribution: powershellКопироватьwsl --unregister <DistributionName>For example: powershellКопироватьwsl --unregister UbuntuThis removes the Linux distribution but not the WSL feature itself. - Disable WSL:
To disable WSL entirely, run the following command in PowerShell: powershellКопироватьdism.exe /online /disable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /norestart - Disable Virtual Machine Platform (If applicable):
If you’re using WSL 2, you also need to disable the Virtual Machine Platform: powershellКопироватьdism.exe /online /disable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /norestart - Disable Hyper-V (Optional):
WSL 2 also uses Hyper-V. To remove it: powershellКопироватьdism.exe /online /disable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Hyper-V-All /norestart - Reboot Your Computer:
After completing these steps, restart your PC to finish removing all WSL components.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Clean Up Remaining Files
Sometimes, after uninstalling, you might want to clean up leftover files and folders:
- Check the
%userprofile%folder:- Open File Explorer and go to
%userprofile%orC:\Users\<YourUsername>. - Delete any remaining WSL-related files or hidden folders like
.wslconfigand.bash_history.
- Open File Explorer and go to
- Check the AppData Folder:
- WSL stores some files in your AppData folder. Go to
C:\Users\<YourUsername>\AppData\Local\Packagesand remove the folder related to the Linux distribution you installed.
- WSL stores some files in your AppData folder. Go to
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4. Remove WSL-Related Registry Entries (Advanced)
If you want to make sure WSL is completely removed, you can edit the registry (be cautious with this step):
- Open Registry Editor:
- Press
Win + R, typeregedit, and press Enter.
- Press
- Navigate to the WSL Registry Entries:
- Go to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Lxssand delete the folder if it exists.
- Go to
- Reboot:
- After modifying the registry, reboot your computer.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5. Optional: Remove Any Associated Software (Optional)
If you installed additional software for WSL, like Docker Desktop for WSL 2, or specific Linux tools, ensure they are uninstalled via the Control Panel or Settings > Apps.
Conclusion
- Uninstall WSL from your Windows computer involves a few steps, which can range from simple removal through Settings to using PowerShell for a full uninstall.
- It’s crucial to disable WSL-related components such as Virtual Machine Platform and Hyper-V if you’re going for a complete uninstallation, especially if using WSL 2.
- After this, you can also clean up any leftover files or registry entries to ensure a clean system.
READ ALSO: Is your AOC monitor OSD locked? [2 ways to unlock it]
