Contents
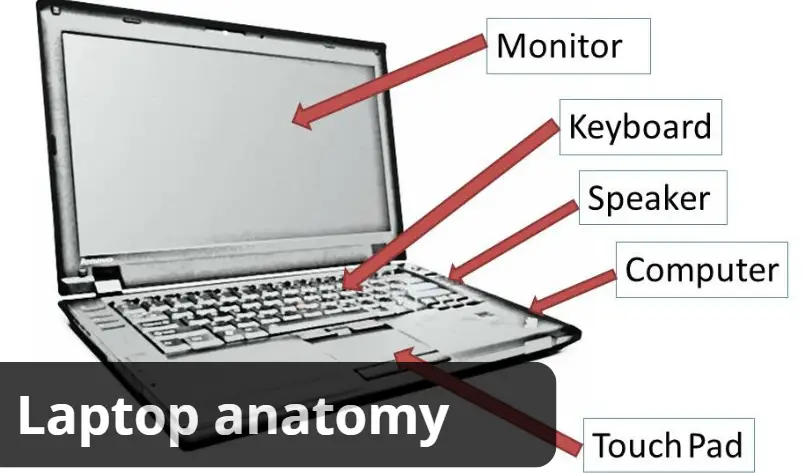
Laptop anatomy
A laptop consists of several main components that contribute to its functionality, both internally and externally. Here’s a breakdown of its key parts:
External Components:
- Screen (Display):
- Usually an LCD or LED screen, where the user views the graphical interface, such as applications, videos, etc.
- Keyboard:
- The input device used for typing, generally integrated into the body of the laptop.
- Touchpad/Trackpad:
- Acts as a mouse, allowing the user to move the cursor and interact with the operating system.
- Ports:
- USB Ports: For connecting peripherals like mice, external storage, or printers.
- HDMI/VGA Ports: For connecting external monitors or projectors.
- Audio Jack: For headphones or speakers.
- Power Connector: Where the charging cable is plugged in.
- Camera:
- A small, built-in webcam generally located at the top of the screen for video conferencing.
- Speakers:
- Built-in speakers, usually placed on the sides or bottom of the laptop for audio output.
- Hinges:
- The mechanical components that allow the screen to open and close.
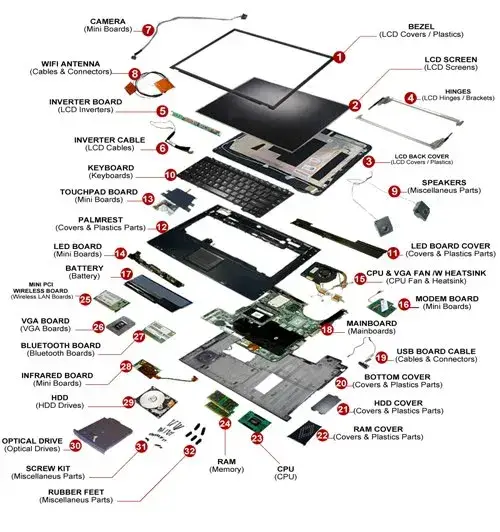
Internal Components:
- Motherboard:
- The main circuit board that connects all components of the laptop, facilitating communication between the CPU, memory, storage, and other devices.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- The brain of the laptop, responsible for executing instructions and running programs.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- Temporary storage used by the CPU to store data that is currently being processed.
- Storage (SSD/HDD):
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or Solid State Drive (SSD): Permanent storage where the operating system, files, and applications are stored.
- Battery:
- Powers the laptop when it’s not plugged into an outlet.
- Cooling System:
- Fans and Heat Sinks: Dissipate heat generated by the CPU and GPU to prevent overheating.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Handles rendering images, videos, and animations. Some laptops have integrated GPUs, while others feature dedicated graphics cards for enhanced performance.
- Wi-Fi Card:
- Provides wireless connectivity to the internet or local networks.
- BIOS/UEFI Chip:
- Basic Input/Output System firmware that starts the laptop and provides low-level control over hardware components.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU):
- Converts electrical energy from the power cord into the appropriate voltage for the laptop’s components.
- Optical Drive (optional):
- Some laptops still feature CD/DVD drives, though they are less common in newer models.
FAQ
Can you use complete anatomy on laptop?
Yes, Complete Anatomy can be used on a laptop, but there are a few things to consider to ensure optimal performance.
System Requirements:
To use Complete Anatomy effectively on a laptop, your device should meet or exceed the software’s minimum or recommended system requirements. Here are the general requirements:
For Windows:
Operating System: Windows 10 (latest build)
Processor: Intel Core i5 or better
RAM: 4 GB (minimum), 8 GB (recommended)
Graphics: Dedicated GPU (NVIDIA or AMD) with at least 2GB VRAM is recommended for better performance, but an integrated Intel GPU will work for simpler tasks.
Storage: 4 GB of free space
For macOS:
Operating System: macOS 10.15 or later
Processor: Intel Core i5 or M1 chip
RAM: 4 GB (minimum), 8 GB (recommended)
Graphics: Apple Silicon (M1 or M2) or a dedicated GPU for Intel-based Macs
Storage: 4 GB of free space
Performance Considerations:
Hardware: A more powerful laptop with a dedicated GPU and higher RAM will provide smoother performance, especially when interacting with 3D models in Complete Anatomy.
Graphics: Rendering detailed 3D anatomy models requires a decent graphics card. Laptops with dedicated GPUs, like NVIDIA or AMD, offer a better experience than those with integrated graphics.
Touchscreen/Trackpad: If your laptop has a touchscreen, the app will be more intuitive to use, especially when zooming in or rotating anatomical models.
How to Get Complete Anatomy:
Windows: Available from the Microsoft Store.
macOS: Available from the Mac App Store.
READ ALSO: How to solve laptop hanging problem?